How to Handle Static Sensitive Devices Like ICs?
Static shocks can destroy ICs in seconds. Don’t let careless handling ruin your electronics. Learn safe practices to protect these delicate components.
Handle ICs with ESD-safe tools, grounded workstations, and wrist straps. Store them in anti-static bags and maintain humidity to prevent static damage.
Want to keep your ICs safe? I’ll share practical tips from my 20 years in ESD protection. Read on to master safe handling.
Why Is Grounding Essential for IC Handling?
Static buildup can zap ICs instantly. Without grounding, you’re risking costly damage. I learned this the hard way early in my career.
Ground yourself with wrist straps and use ESD mats. Grounded workstations dissipate static, protecting ICs from harmful discharges during handling.
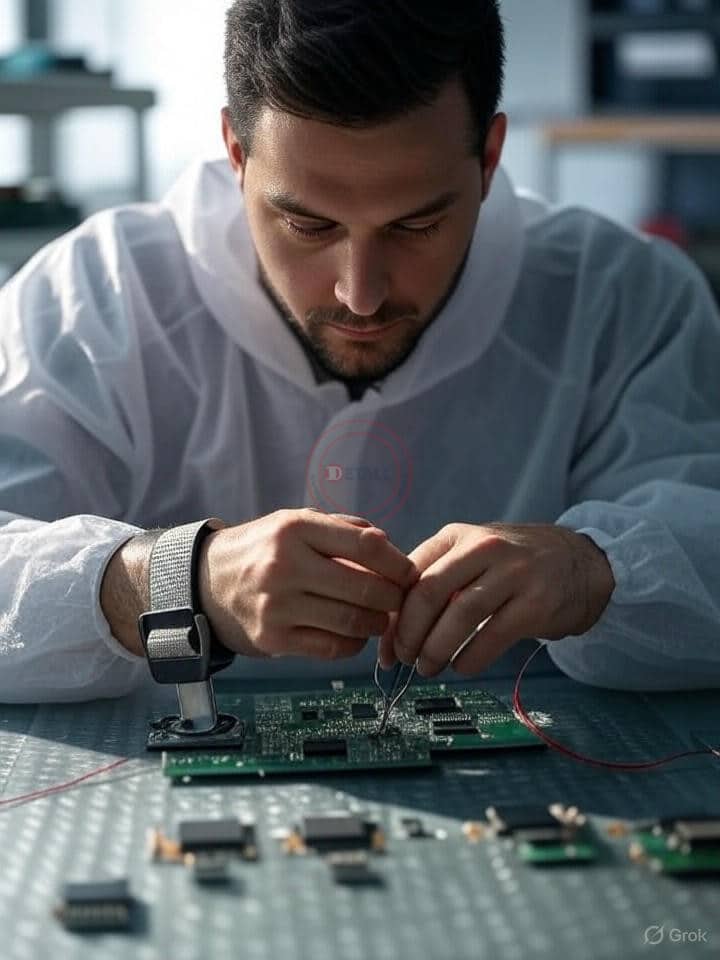

Grounding is your first defense against ESD. ICs, with their tiny circuits, can fail from a spark you don’t even feel. I once saw a technician skip a wrist strap, frying a batch of microchips—expensive mistake! Our factory’s ESD workbenches, compliant with IEC61340-5-1, have built-in grounding points. Here’s how grounding protects ICs:
| Grounding Tool | Purpose | Best Practice |
|---|---|---|
| Wrist Straps | Connects you to ground | Wear snugly, test daily |
| ESD Mats | Dissipates static on surfaces | Use on workbenches, clean regularly |
| Grounded Workbenches | Ensures consistent grounding | Check connections, modular design |
Test grounding equipment daily. A faulty strap or mat can let static sneak through, damaging your ICs.
How Do Anti-Static Storage Solutions Help?
ICs left exposed are static magnets. Poor storage can ruin them before use. Proper containers make all the difference.
Store ICs in anti-static bags or conductive containers. These shield against static buildup, keeping components safe until needed.
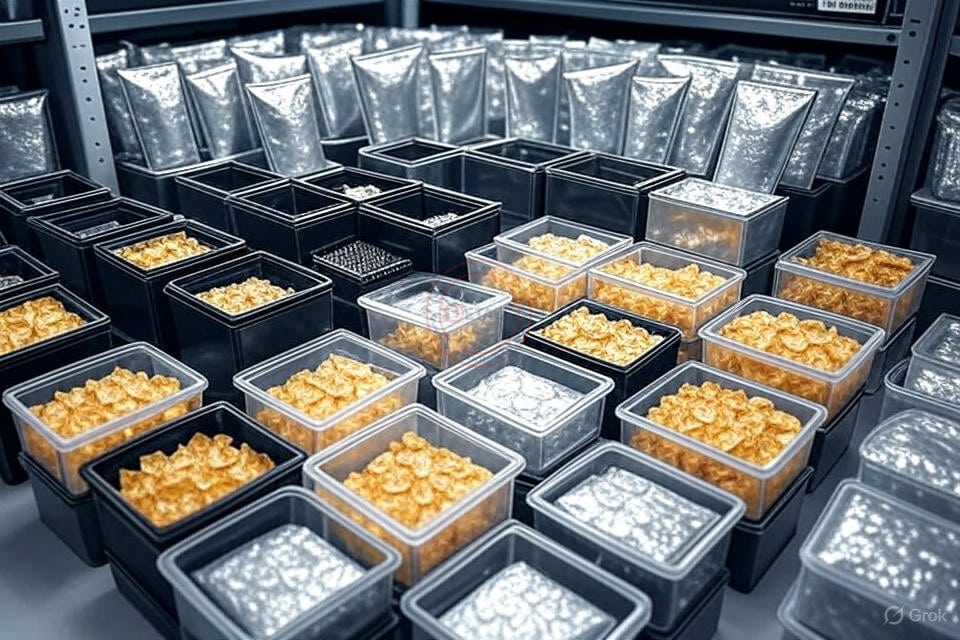

Anti-static storage is critical. ICs are vulnerable even when idle. I recall a project delayed because unprotected chips failed during assembly. Our modular ESD workbenches include quick-hang storage for easy access to shielded containers. Here’s a breakdown of storage options:
| Storage Type | Protection Level | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Anti-Static Bags | High | Transport, short-term storage |
| Conductive Boxes | Very High | Long-term storage, sensitive ICs |
| Shielding Trays | Moderate | Assembly line, quick access |
Use conductive materials for maximum protection. Label containers to avoid mix-ups, and never store ICs in regular plastic bags—they generate static.
Can Environmental Controls Prevent ESD Damage?
Static thrives in dry air. Uncontrolled environments can harm ICs. Simple changes to your workspace can reduce risks.
Maintain 40-60% humidity and use ionizers. These neutralize static charges, creating a safe environment for handling ICs.

Humidity and air quality matter. Dry air boosts static, while high humidity dissipates it. I’ve seen production lines halt because low humidity caused ESD failures. Our CE-certified ESD workbenches pair with ionizers for optimal control. Here’s how to manage your environment:
| Control Method | Effect | Implementation |
|---|---|---|
| Humidifiers | Raises humidity to safe levels | Set to 40-60%, monitor daily |
| Ionizers | Neutralizes static in air | Place near workstations, maintain |
| Temperature Control | Stabilizes humidity | Keep at 20-25°C, avoid extremes |
Check humidity daily with a hygrometer. Combine with grounded tools for a foolproof ESD-safe zone, protecting ICs during handling.
Are ESD-Safe Tools Necessary for ICs?
Using regular tools on ICs is risky. Static from ungrounded tools can cause invisible damage. Specialized tools are a must.
Use ESD-safe tweezers, screwdrivers, and pliers. These tools prevent static transfer, ensuring safe handling of ICs.
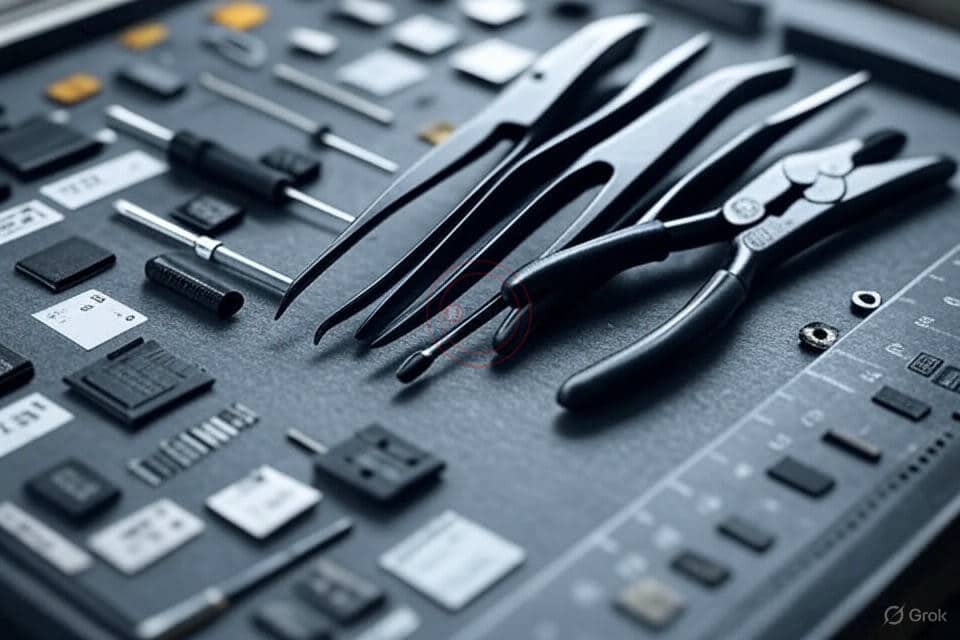

ESD-safe tools are non-negotiable. Regular tools can carry static, damaging ICs’ delicate circuits. I once traced a circuit failure to a cheap screwdriver—lesson learned. Our workbenches’ modular tool racks keep ESD-safe tools organized. Here’s a tool guide:
| Tool Type | ESD-Safe Feature | Usage Tip |
|---|---|---|
| Tweezers | Conductive coating | Grip ICs gently, avoid pins |
| Screwdrivers | Grounded handle | Use for PCB assembly, store safely |
| Pliers | Anti-static material | Handle larger ICs, check grounding |
Store tools in ESD-safe holders. Regular maintenance ensures they stay effective, keeping your ICs safe during assembly or repair.
Conclusion
Grounding, anti-static storage, environmental controls, and ESD-safe tools are key to handling ICs. Use these practices to protect sensitive devices and ensure reliability.



