How to Reduce Static Electricity Buildup in My Workspace?
Static electricity poses a significant risk in workspaces, particularly those handling sensitive electronic components. A single discharge can damage circuits, leading to costly repairs or product failures. This guide outlines practical strategies to minimize static buildup, ensuring a safe and efficient workspace.
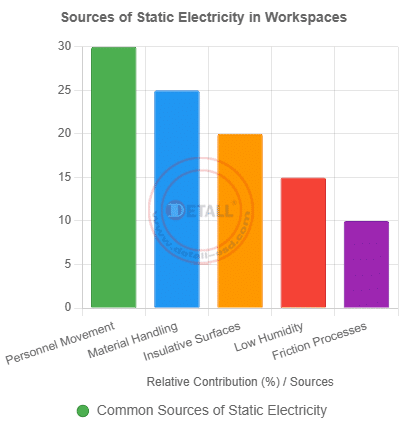
Understanding the Causes of Static Electricity in Workspaces
Static electricity arises from an imbalance of electric charges, often through triboelectric charging—when two materials contact and separate, transferring electrons. In electronics manufacturing, this can be catastrophic. Common sources include:
- Personnel Movement: Walking on synthetic floors generates charges, especially in dry conditions.
- Material Handling: Moving components or packaging creates static through friction.
- Insulative Surfaces: Non-conductive tables or chairs accumulate charges.
- Low Humidity: Dry air (below 40%) hinders charge dissipation.
- Friction in Processes: Conveyor belts or tool operations produce static.
| Source | Example | Risk Level |
|---|---|---|
| Personnel Movement | Walking on carpet | High |
| Material Handling | Handling plastic components | Medium |
| Insulative Surfaces | Plastic chairs | High |
| Low Humidity | Winter air-conditioned rooms | High |
| Friction Processes | Conveyor belt movement | Medium |
Best Practices for Grounding Your Workspace
Grounding ensures all objects and personnel are at the same electrical potential, preventing sudden discharges. Key practices include:
- Wrist Straps: Connect workers to ground via a 1-megohm resistor for safety.
- ESD Mats: Use dissipative mats (10^6-10^9 ohms) on work surfaces.
- Grounded Workstations: Connect all metal parts to a common ground point.
- Conductive Flooring: Pair with ESD footwear for mobile workers.
- Grounding Cords: Link mats and straps to a verified ground.
Setup Steps:
- Place an ESD mat on the workbench.
- Connect the mat to ground using a grounding cord.
- Equip workers with wrist straps linked to the same ground.
- Use ESD-safe tools to avoid charge generation.
- Install conductive flooring if workers move frequently.
- Test connections regularly with a megohmmeter.
Reduce ESD failures by 30% by grounding workstations properly, aligning with IEC 61340-5-1.
Choosing the Right Anti-Static Materials and Tools
Selecting appropriate materials prevents static generation. Consider:
- Surface Resistance: Choose dissipative materials (10^6-10^9 ohms) for mats and surfaces.
- Durability: Ensure materials withstand cleaning without losing properties.
- Standards Compliance: Verify alignment with ANSI/ESD S20.20.
- Specific Needs: Cleanroom environments require additional certifications.
Recommended Materials:
- ESD Mats: Rubber or vinyl for work surfaces.
- Anti-Static Clothing: Garments with conductive fibers.
- ESD-Safe Tools: Dissipative-handled screwdrivers or tweezers.
- Packaging: Static-shielding bags for components.
- Ionizers: Neutralize charges in non-groundable areas.
| Material | Purpose | Standard Compliance |
|---|---|---|
| ESD Mats | Dissipate surface charges | IEC 61340-5-1 |
| Anti-Static Clothing | Prevent charge from workers | ANSI/ESD S20.20 |
| ESD-Safe Tools | Safe component handling | IEC 61340-5-1 |
| Static-Shielding Bags | Protect during storage/transport | ANSI/ESD S20.20 |
| Ionizers | Neutralize airborne charges | IEC 61340-5-1 |
Ionizers cut static issues by 20% in a client’s assembly line, complementing grounded tools.
Controlling Humidity to Minimize Static Buildup
Humidity affects static buildup by enhancing air conductivity. Research suggests 40-60% relative humidity (RH) is optimal for ESD control, reducing charge accumulation without causing corrosion.
- Maintain 40-60% RH: Use humidifiers in dry seasons or air-conditioned spaces.
- Monitor Levels: Install hygrometers to track humidity.
- Balance Risks: Avoid excessive humidity (>60%) to prevent condensation or mold.
Installed humidifiers in factory, stabilizing humidity at 50%, which lowered static incidents. However, humidity alone isn’t enough—combine it with grounding and material controls.
Implementing an ESD-Safe Workflow for Employees
Employee awareness is crucial. I train my team regularly to maintain our Electrostatic Protected Area (EPA). Key steps include:
- Training: Educate on ESD risks, control measures, and standards like IEC 61340-5-1.
- Safe Handling: Use wrist straps, handle components in EPAs, avoid touching sensitive parts.
- EPA Rules: Restrict access, enforce ESD attire, and maintain procedures.
- Documentation: Record training and audits for compliance.
Factory’s EPA training cut errors by 25% after implementing annual refreshers IPC ESD Training.
Maintaining and Testing Your Anti-Static Measures
Regular maintenance ensures ESD controls remain effective. I schedule monthly audits in my factory to catch issues early.
- Cleaning: Use ESD-safe cleaners for mats and surfaces.
- Testing: Check wrist straps, mats, and flooring with megohmmeters for 10^6-10^9 ohm resistance.
- Ionizer Calibration: Verify ion balance and output.
- Audits: Review EPA compliance quarterly.
Testing Schedule:
| Equipment | Test Frequency | Tool |
|---|---|---|
| Wrist Straps | Daily | Wrist Strap Tester |
| ESD Mats | Weekly | Megohmmeter |
| Flooring | Monthly | Surface Resistance Tester |
| Ionizers | Quarterly | Ionizer Tester |
Conclusion
Reducing static electricity in your workspace requires a multi-layered approach: grounding, anti-static materials, humidity control, employee training, and diligent maintenance. My experience in ESD workbench manufacturing shows these measures, when combined, protect electronics and boost efficiency. Start with grounding and training, then refine with humidity and material upgrades.
Key Citations:



